HSS vs HS
An overview of flash sync technology
Demystifying Hi-Sync and HSS flash.
Going beyond 1/200th Second.
Since the dawn of photography, there have always been technical limitations that restricted how and where flash could be used to enhance an image. In the last few years, there has been a slew of innovations with different flash technologies that have opened up never before possible options.
These advanced flash techniques are often misunderstood. The aim of this post is to demystify and define the various flash technologies that allow us to shoot at shutter speeds higher than the standard flash sync speed of DSLR and mirrorless cameras.
HyperSync, HighSpeedSync, Hi-Sync.
All these flash techniques are misunderstood.

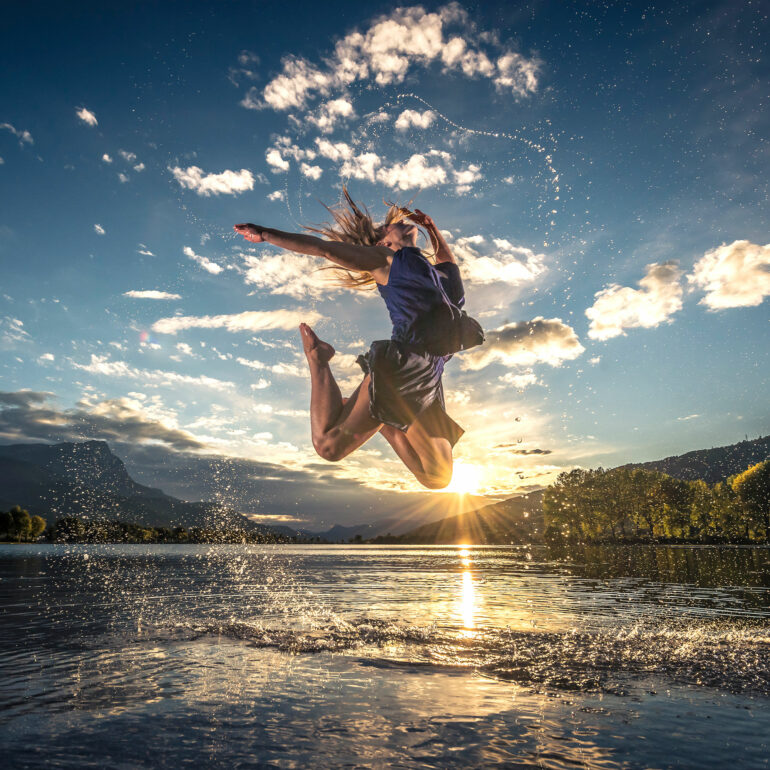
With a fast shutter speed you can darken the background. ELB 400 + Pro Head - 1/2500th sec - f/2.8 - ISO 200
What is Flash Sync?
An Overview of Flash Sync with Cameras.
All flashes, no matter what size or shape, work by storing up an electrical charge and then emitting that charge as a light source through a flash tube.
When the flash is triggered the electrical charge is dumped into the flash tube and ignites a gas. The gas is ionized and thus releases a flash of light. Hence, the flashes we use these days are just a modern version of the old-time flashes used a century ago where photographers basically ignited flash powder to create light.
We are still just igniting a chemical substance. The only difference now is that we can control the amount of light emitted by the flash electronically and with incredible accuracy.
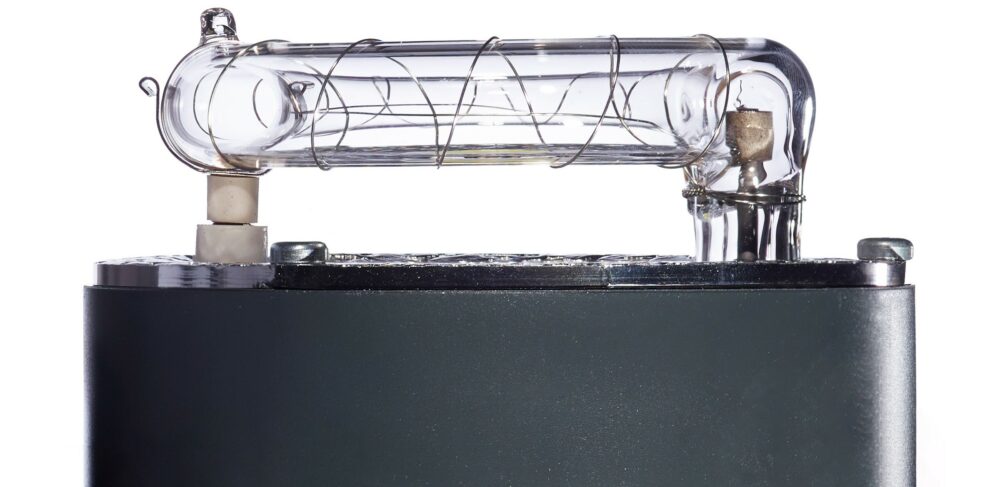

Hi-Sync is the result of an optimized flash tube and remarkable technology built into the Transmitter Pro.
How modern flashes work is simple in theory but complex in execution.
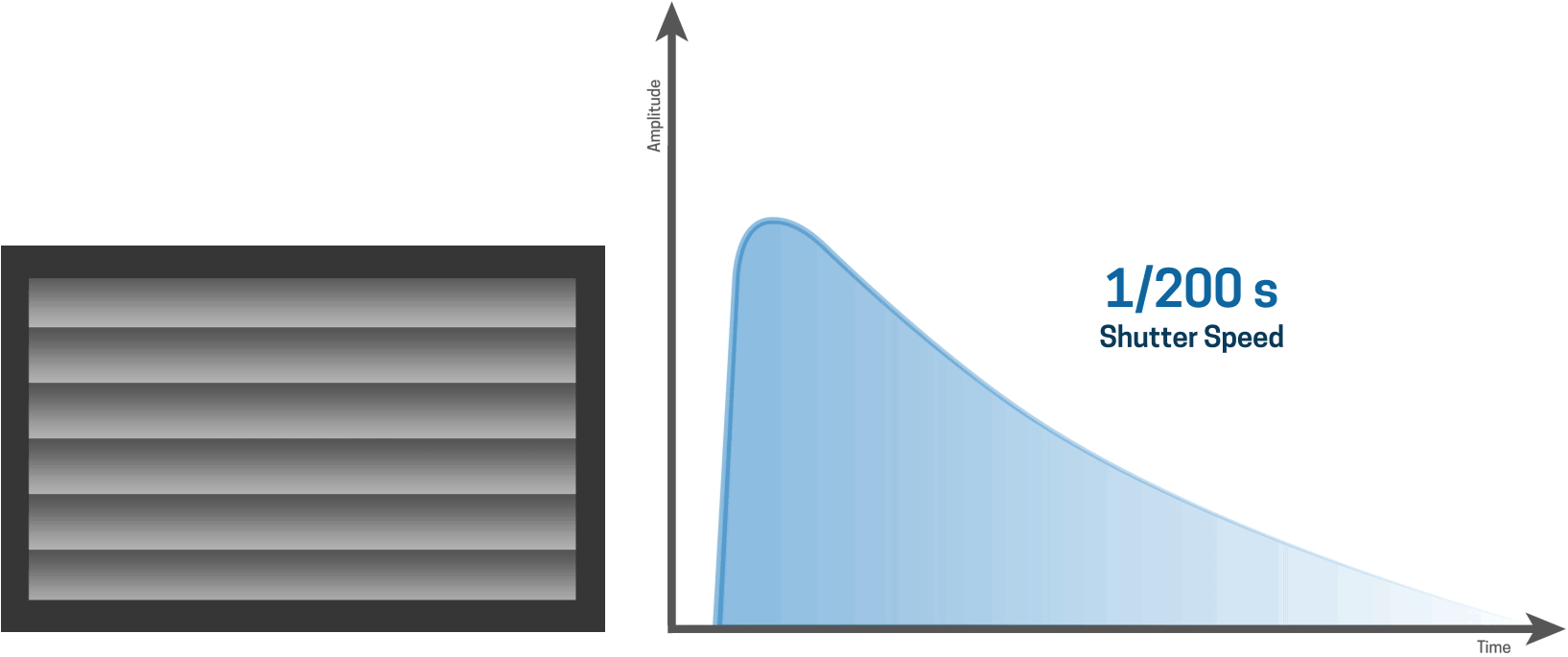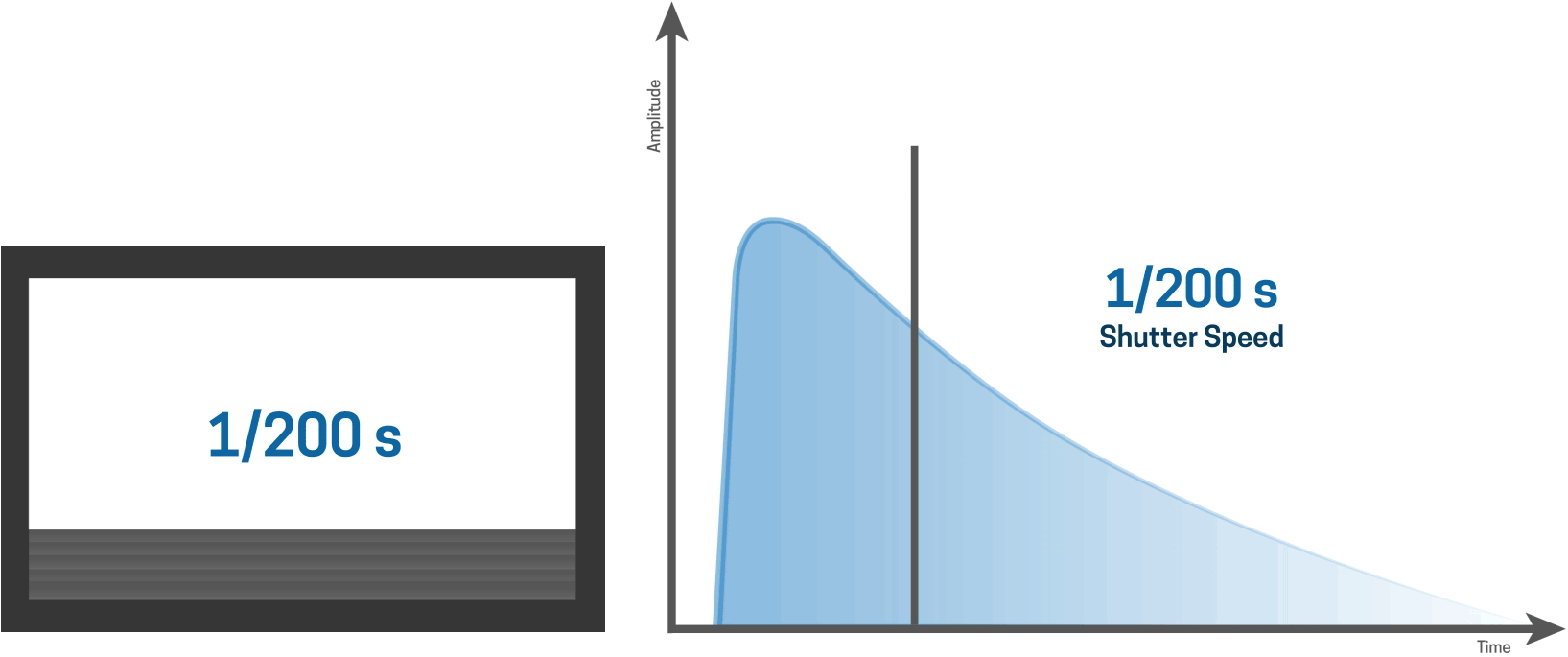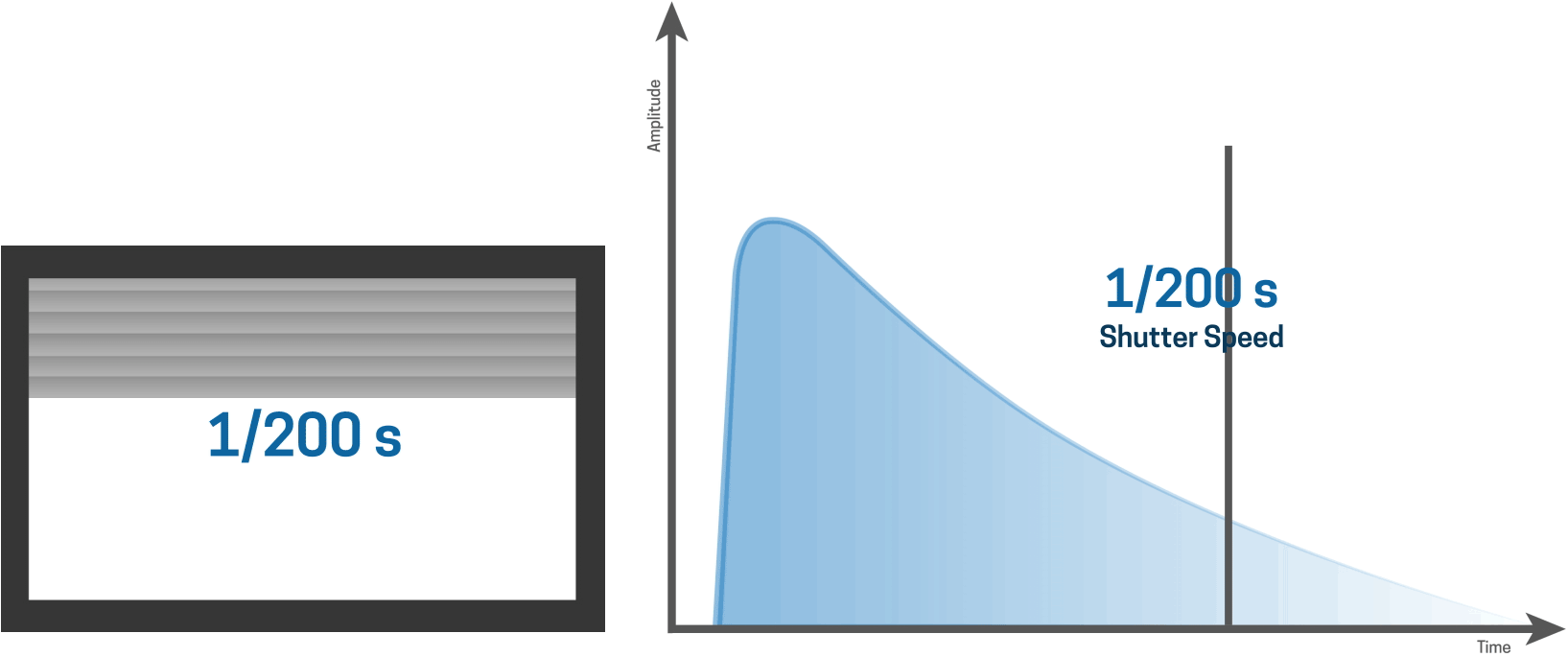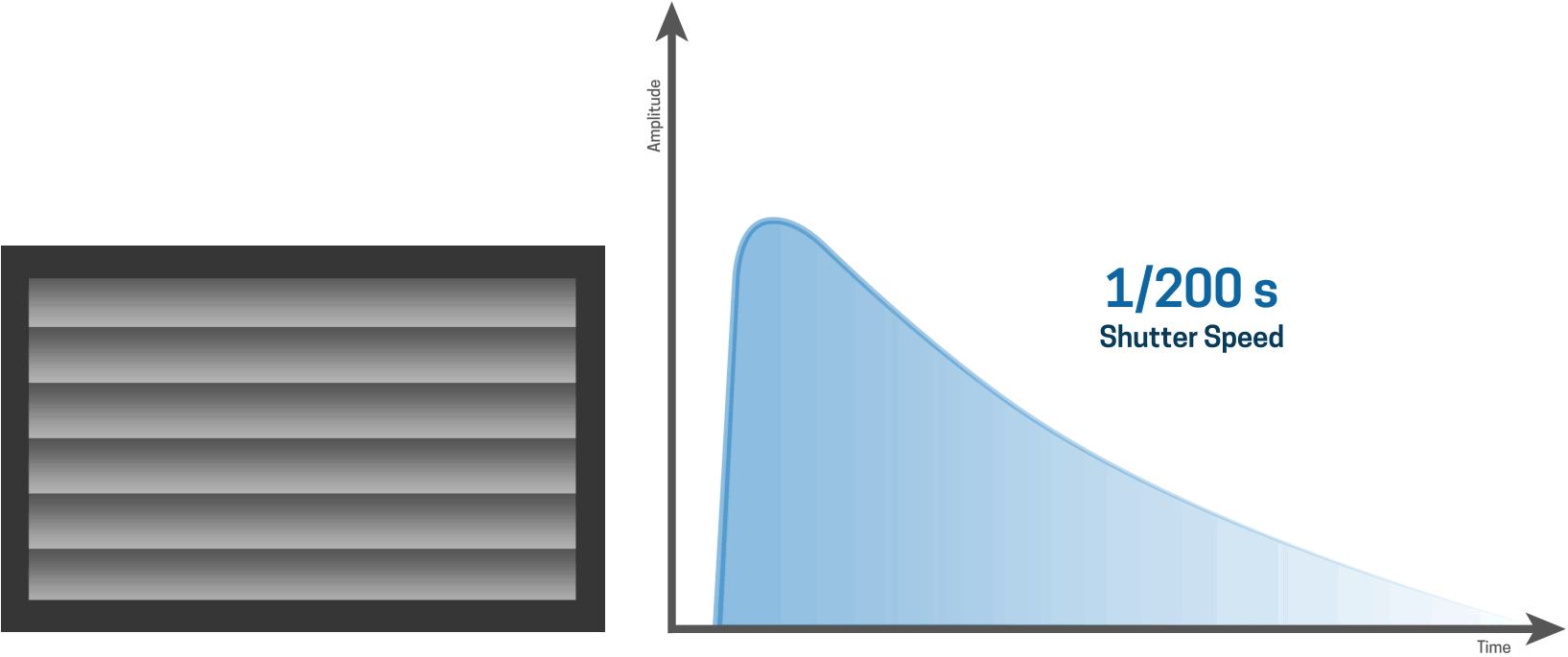
At 1/200s the sensor is fully exposed with flash
The focal-plane shutter incorporated into most modern DSLRs is composed of two separate parts, the first curtain and the second curtain.
When you press the shutter release the first curtain opens and then the second curtain closes according to the selected shutter speed.
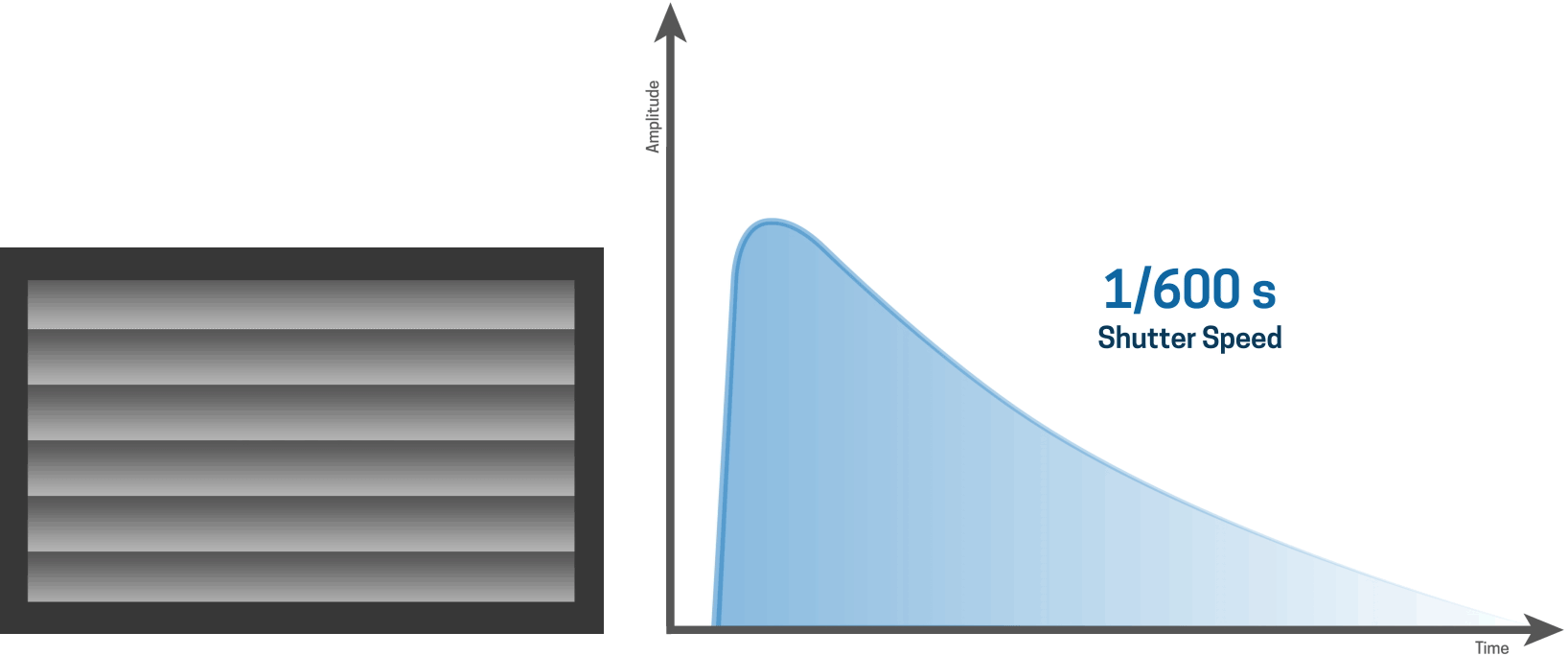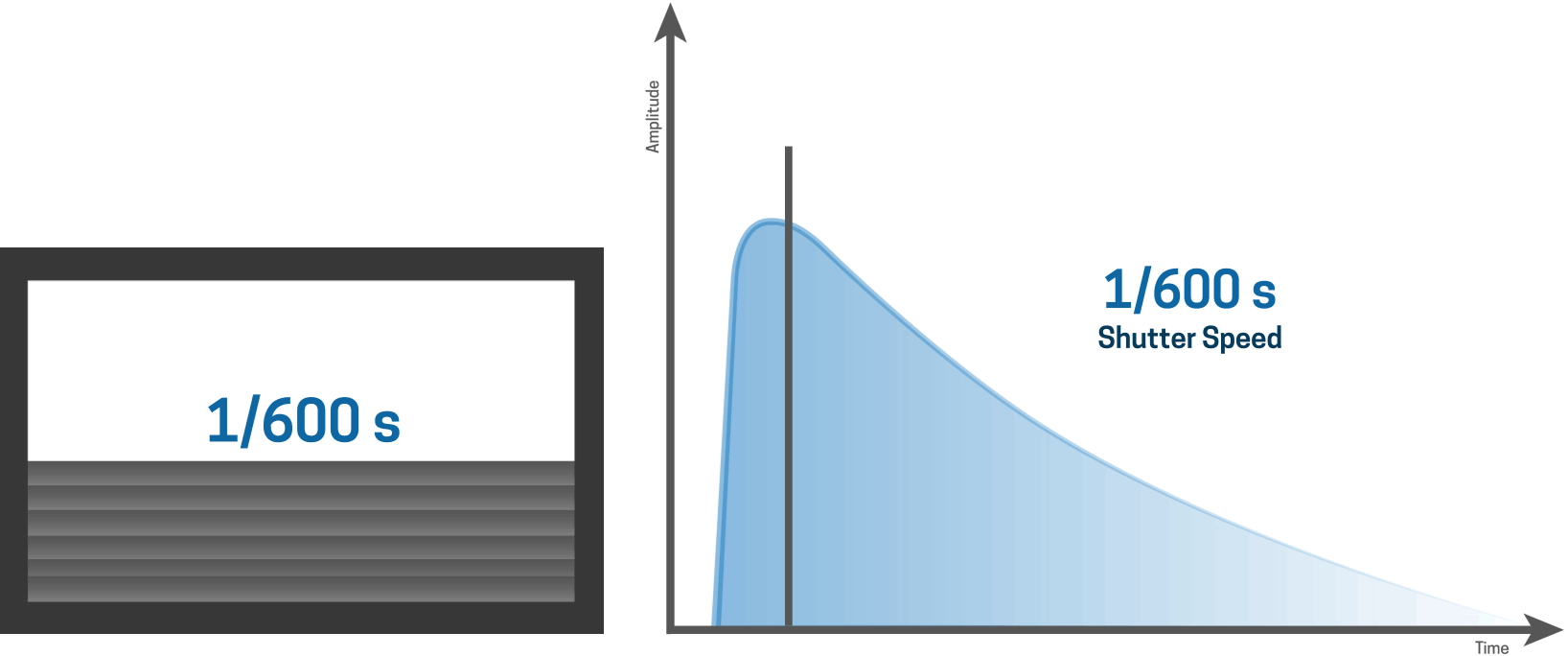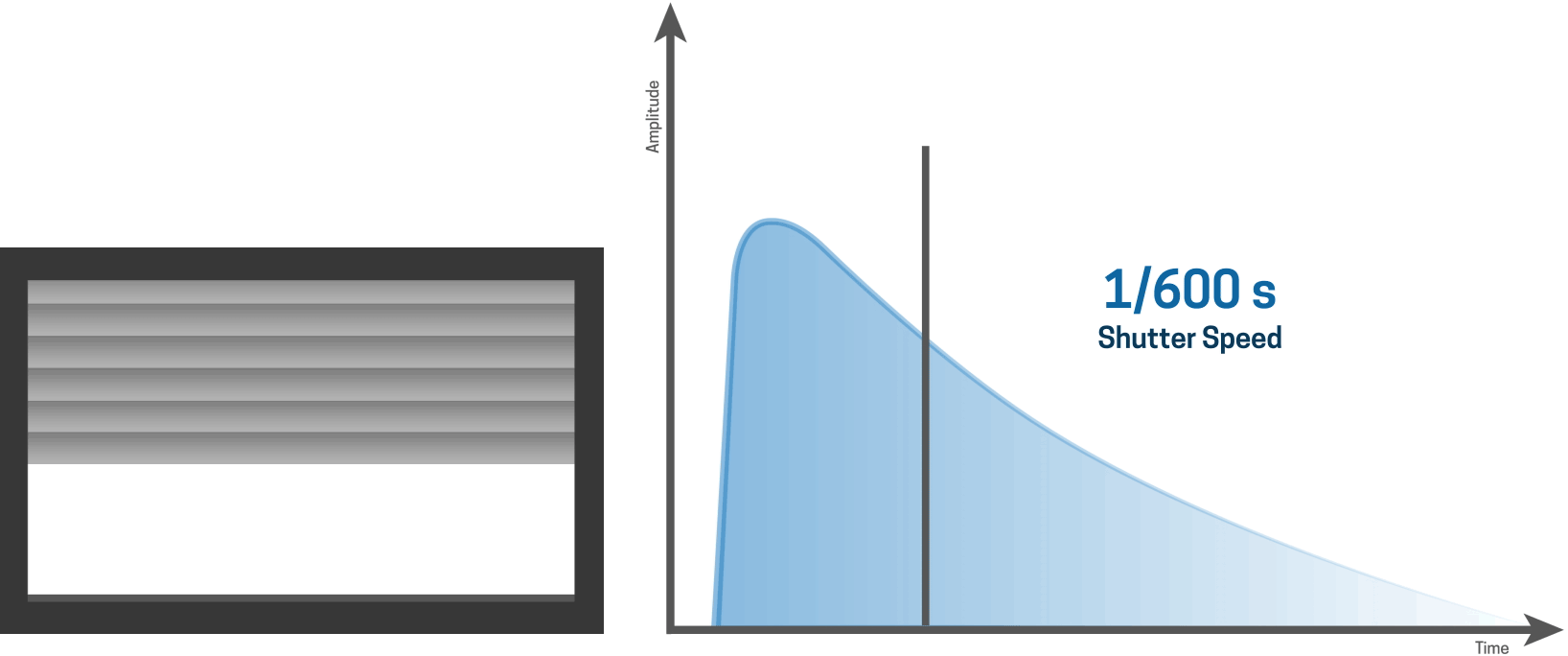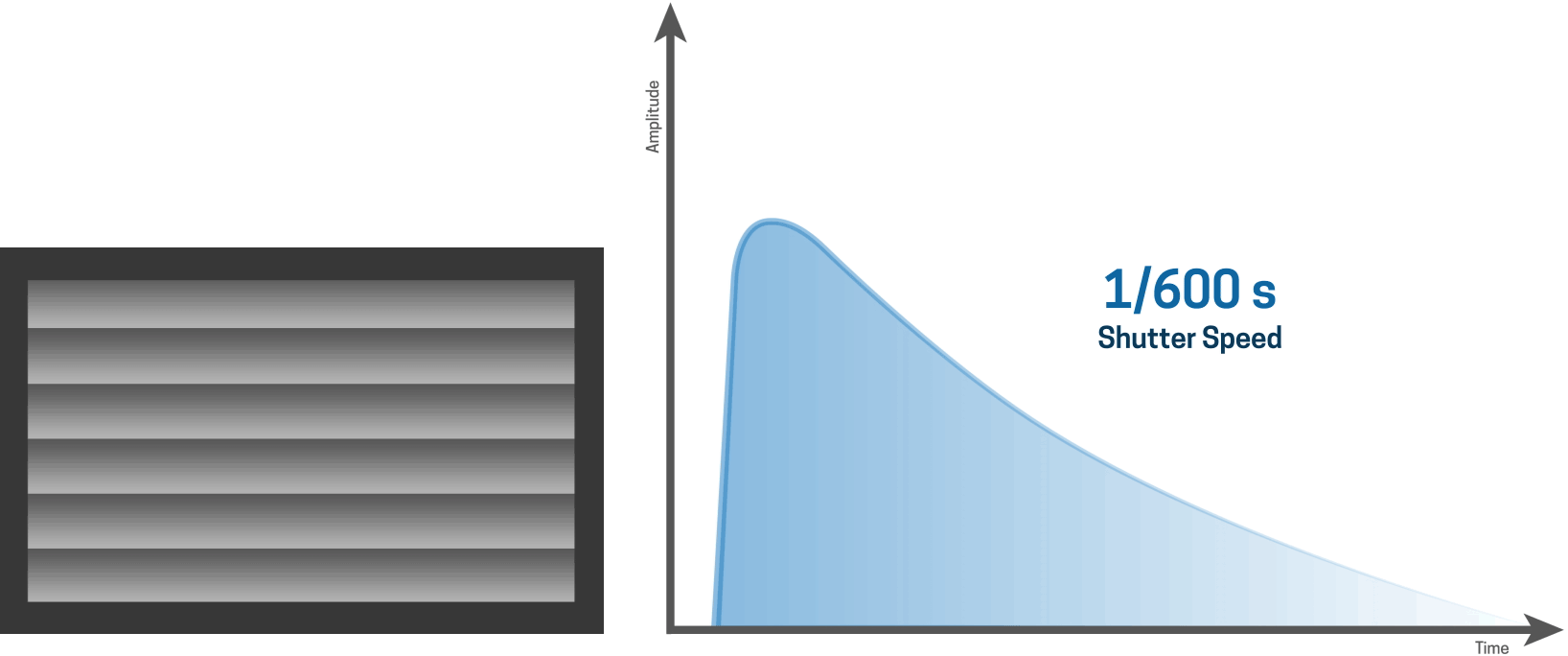
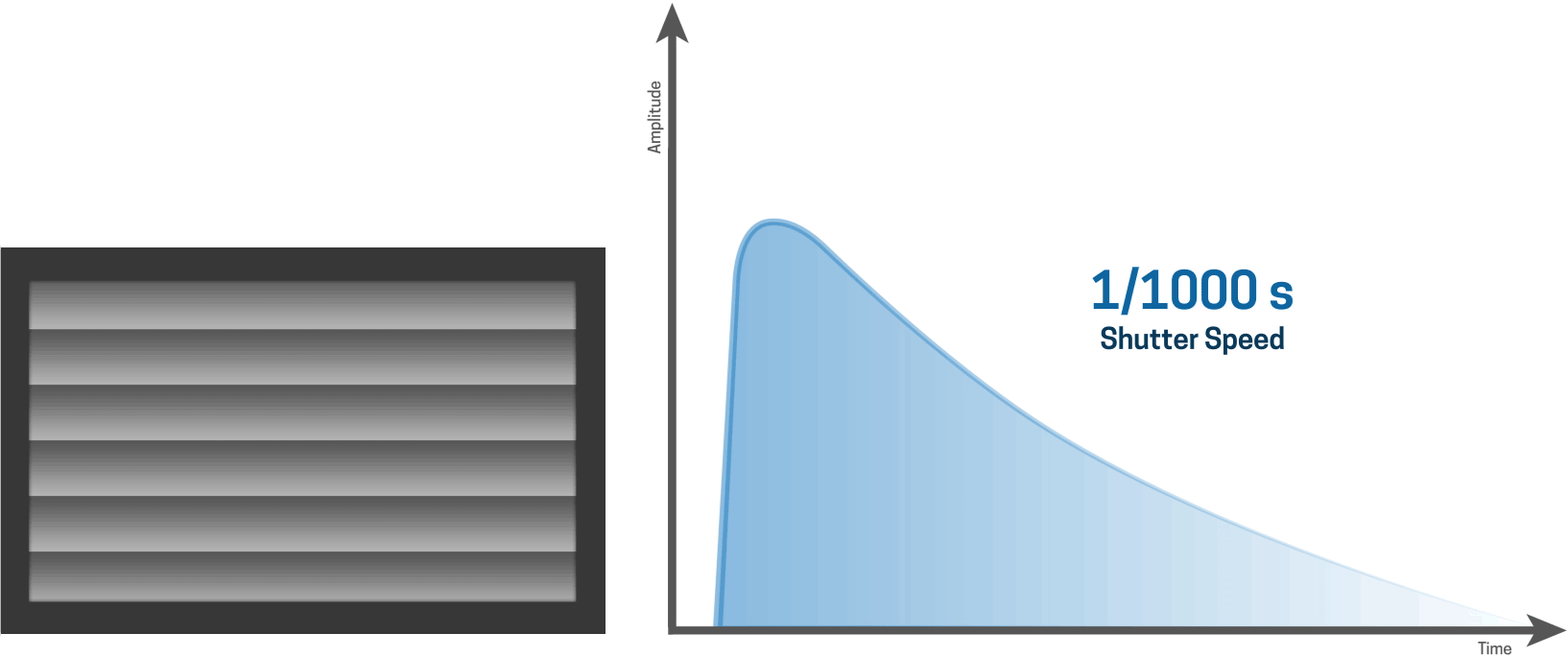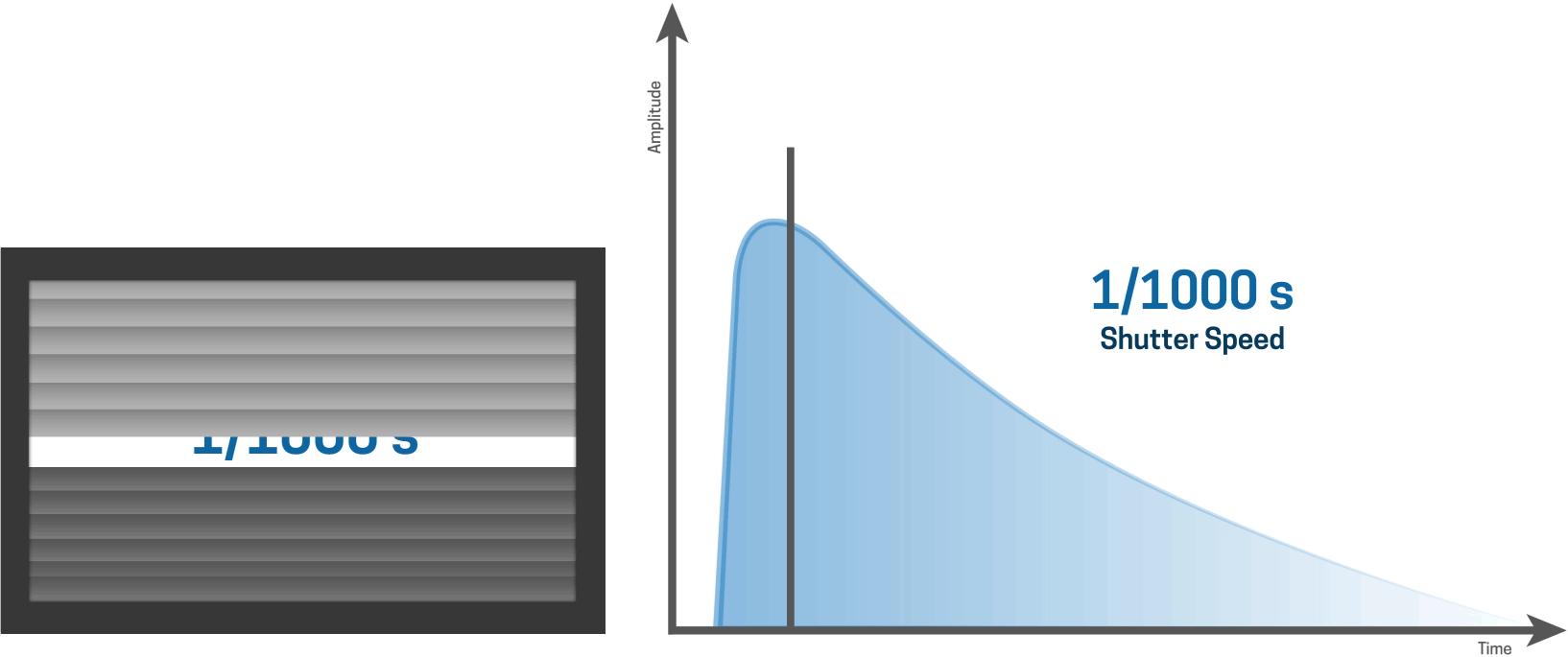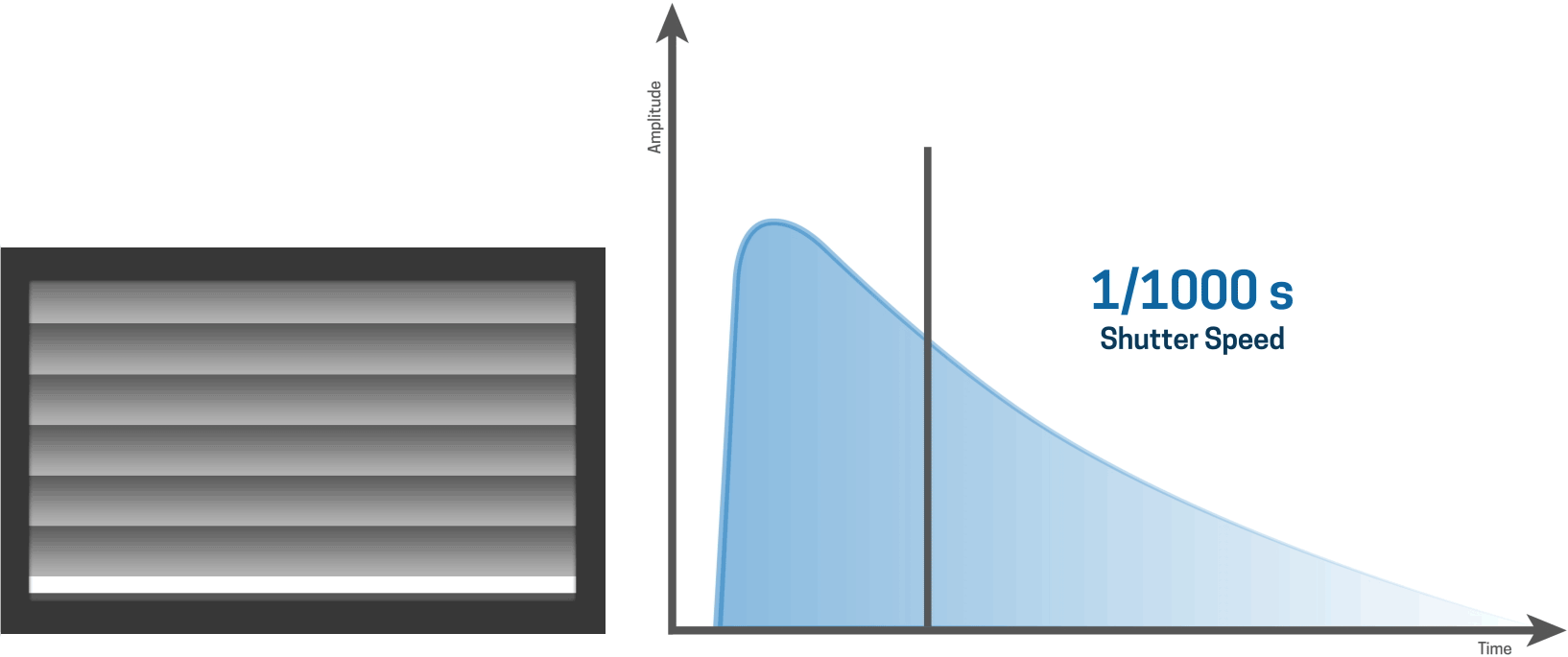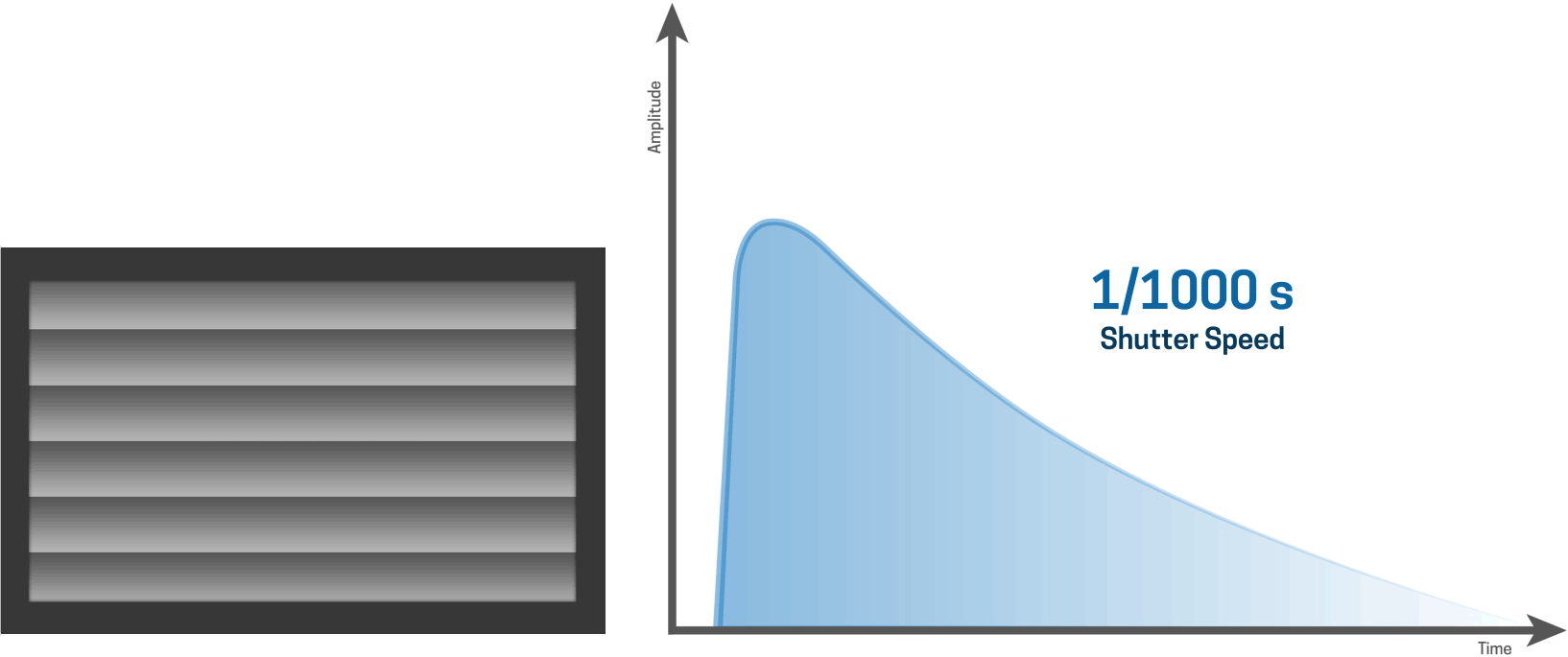
As the shutter speed gets shorter...
The time gap between the first and second curtain is the shutter speed.
For longer shutter speeds, like a one second shutter speed for example, the first curtain opens and the second curtain closes after the one-second time period has elapsed. In this case, the entire sensor is exposed to the light between the opening of the first curtain and the closing of the second curtain.
... it is apparent that a slit is moving over the sensor.
For shorter shutter speeds, like a 1/1000 second shutter speed, the first curtain starts to open and the second curtain follows shortly thereafter before the first curtain has made it’s way across the entire sensor.
This results in a narrow slit of light that moves over the sensor, thereby creating a very fast shutter speed.
The “flash sync” is how the camera synchronizes with the flash so that the light emitted by the flash is recorded on the imaging sensor.

The highest flash sync speed of any camera is the fastest shutter speed at which the entire sensor is exposed completely to the burst of light. For some DSLRs, the flash sync speed is 1/200th second while others go up to 1/320th second.
As an example, with a Nikon D810, the top flash sync speed with strobes is 1/250 second. This is the fastest shutter speed where the entire sensor is exposed all at once. With shutter speeds higher than 1/250 second, the entire imaging sensor is not exposed at any point, which is why you see a black bar in the bottom of the frame if you try to shoot at a shutter speed above the standard flash sync. That black bar is the shadow of the second curtain closing.

ELB 1200 + Action flash head - 1/800th sec - f/5 - ISO 100
Some medium format cameras have leaf shutters that are built into the lens, and which work differently than the vertical plane shutters in DSLRs. These shutters allow for higher flash sync speeds (in some cases up to 1/1,600 second) with no clipping.
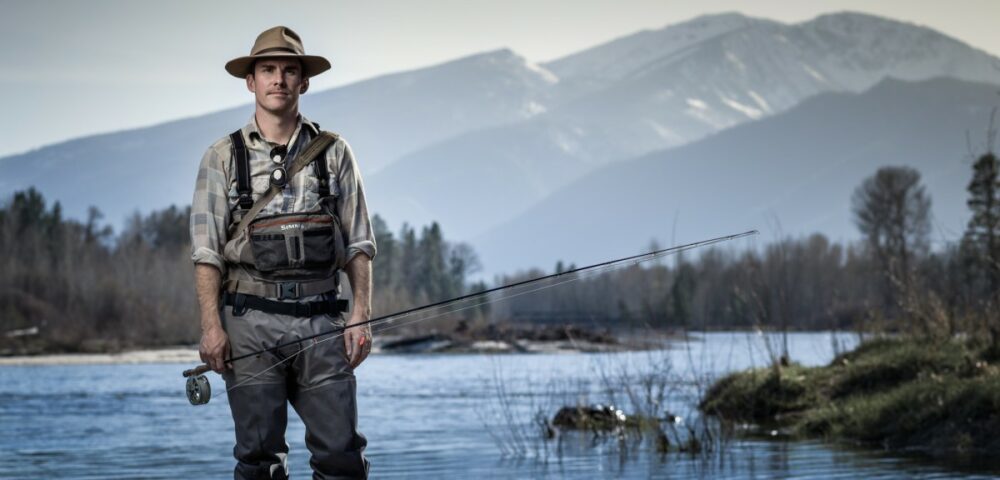
This portrait of a fly-fisherman was captured with a Hasselblad H5D medium format digital camera using a leaf shutter, which can sync with flash at every shutter speed.
Medium format cameras have traditionally been the go-to option when needing to sync with flash at high shutter speeds because they have a completely different shutter mechanism.
For What?
Why do we need to shot in High Speed Sync?
For photographers, especially those working outdoors, the 1/250th second flash sync speed represents a huge limitation.
When shooting with strobes, the aperture controls the brightness of the light on your subject and the shutter speed controls the brightness of the background.
Hence, if your subject is overexposed you stop down the aperture. If your background is too bright you can choose a faster shutter speed to darken the background or a slower shutter speed to brighten the background.
When shooting outdoors, in broad daylight, being restricted to a shutter speed or 1/200th or 1/250th second means that quite a bit of flash output (Watt-seconds) is required to overpower daylight.
By accessing higher shutter speeds, we can overpower daylight with less flash power (or from farther away) and we also have
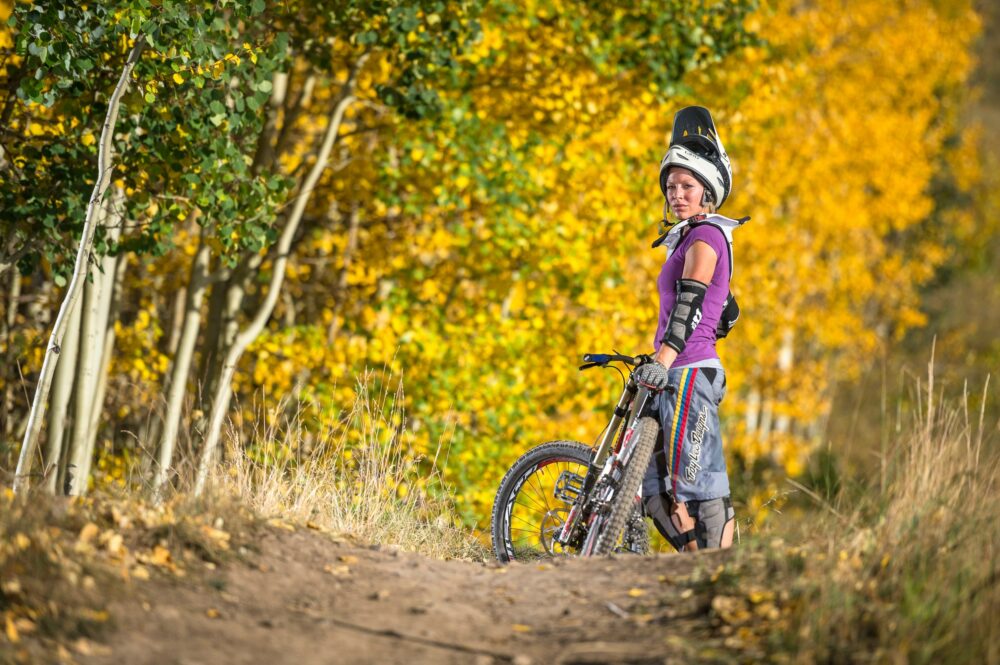

2x ELB 400 + Pro Head - 1/5000th sec - f/2.8 - ISO 200
Complete freedom to use whatever shutter speed and aperture combination you want with flash.
The main reasons to use Hi-Sync and HSS flash technologies are:
- Use a high shutter speed to freeze motion.
- Overpower the sun with less flash power and lighter gear.
- Use flash with a large aperture and create a narrow depth of field.
- Darken backgrounds using a high shutter speed.
Working with both HS and HSS flash technologies opens up new doors creatively allowing for full control over the final image when using flash.
2 Technologies
Hi-Sync and HSS
As of this moment, the two predominant technologies on the market that allow for working with flash above the normal flash sync speed are High Speed Sync (HSS) and Hi-Sync (HS).
Let’s discuss each of these in detail and explain how they work.
High Speed Sync (HSS)
High Speed Sync is a technology invented for Speedlights, now used by several manufacturers and implemented in the latest ELB 500 TTL.
HSS works by continuously pulsing the flash at incredibly high speeds creating a stroboscopic effect that illuminates the shutter slit as it moves down the sensor. Because it has to output so many pulses of light, creating essentially a continuous light source for a brief period of time, the actual light output of the flash is quite low and can vary wildly depending on the shutter speed.
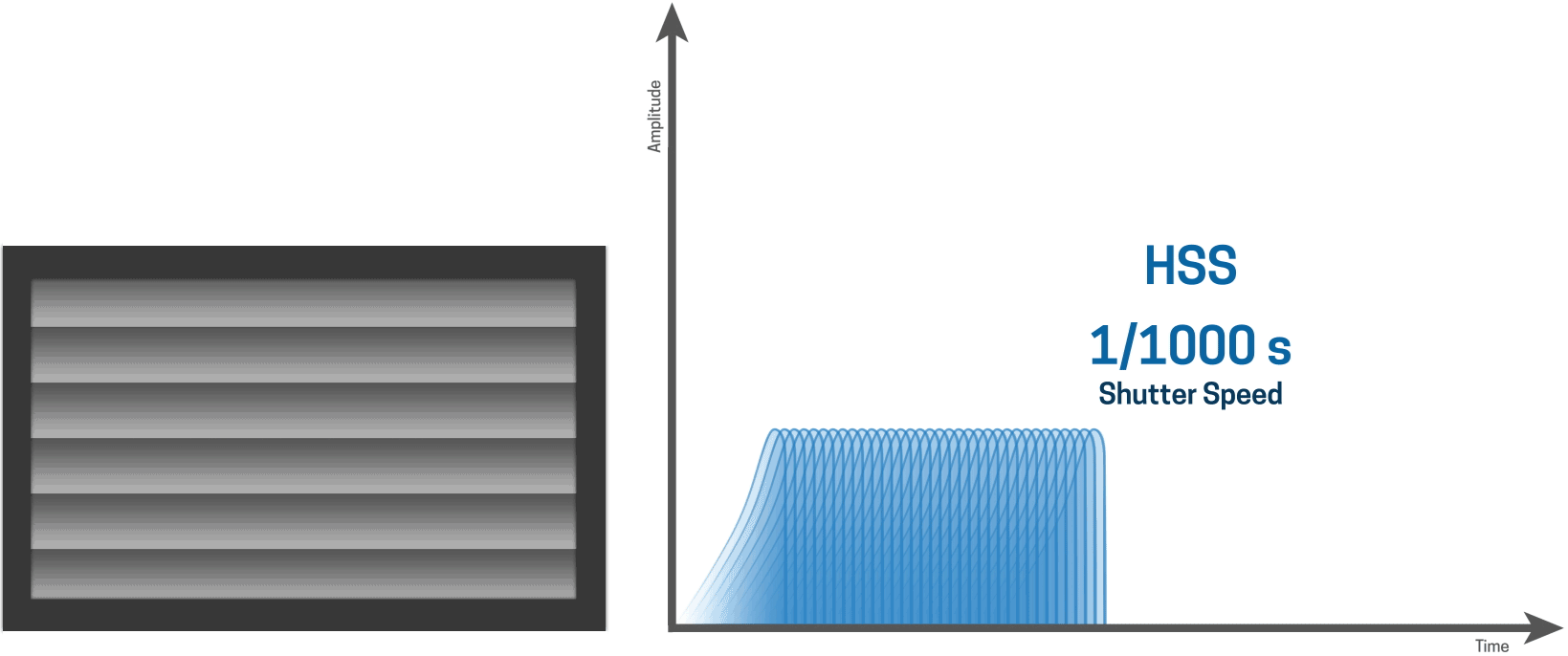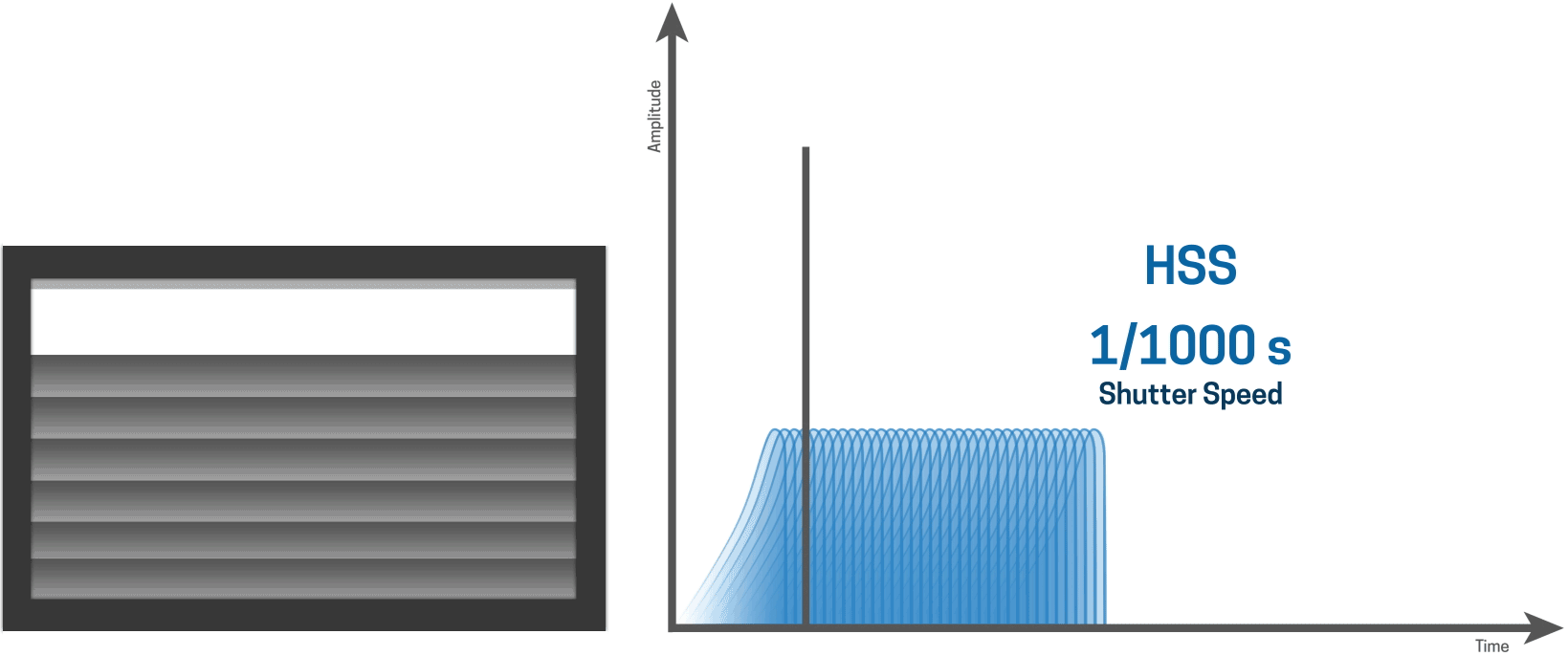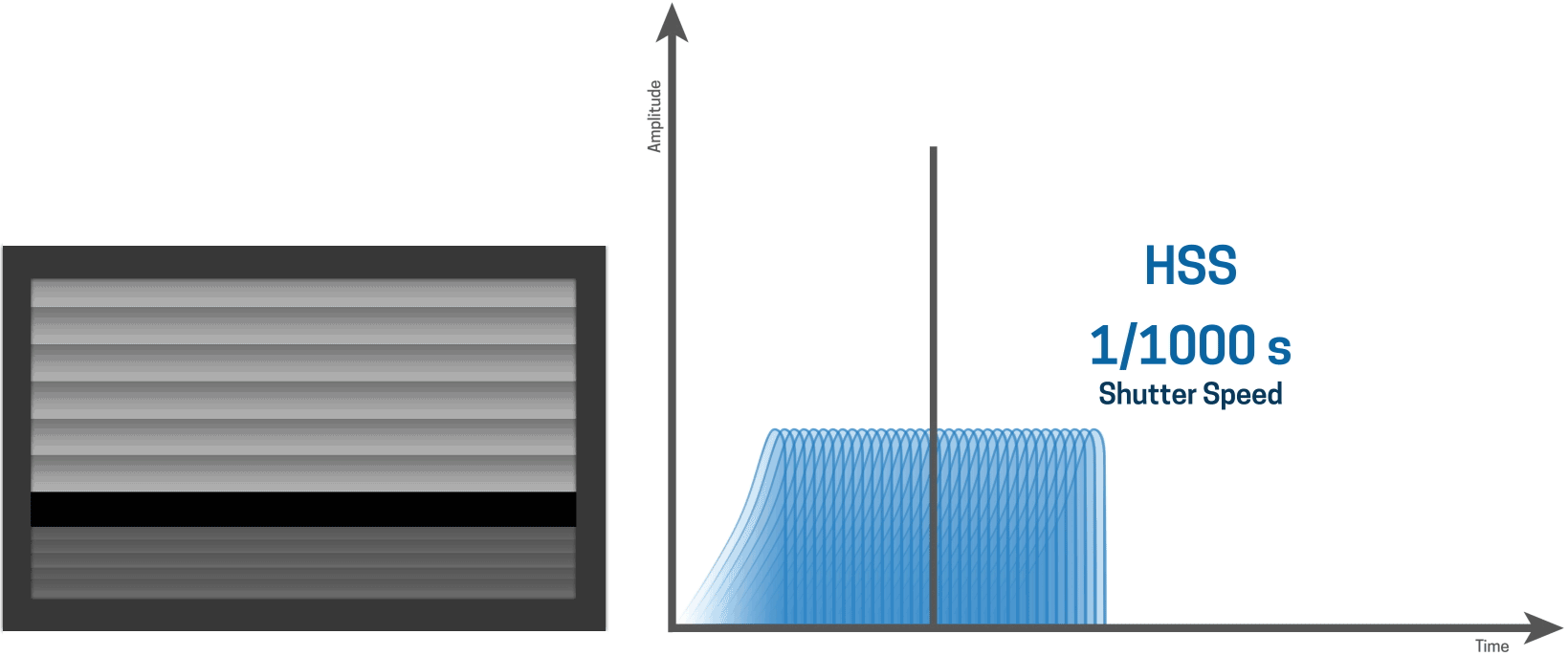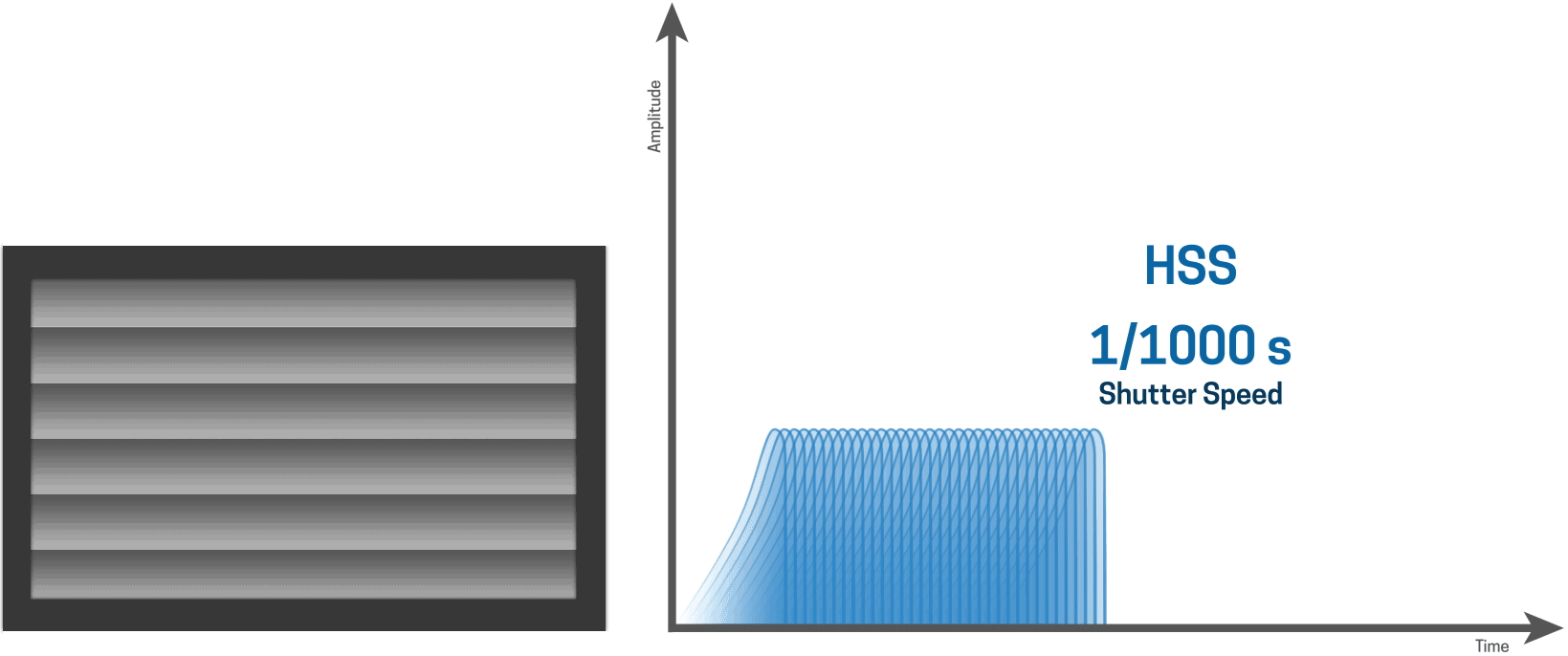
HSS works by firing the flash at low power thousands of times per second, which basically creates a continuous light source. The pulses of light illuminate the entire image as the shutter slit.
HSS creates consistent lighting across the entire image
The upside of HSS is that it creates very consistent lighting across the entire image.
The downside is that because the flash is outputting so many bursts of light in such a short period, the flash has to be fairly close to the subject. The light output also decreases with faster shutter speeds.
Even so, since HSS technology is usually paired with TTL technology, it works very effectively and is also incredibly easy to use.
For wedding, fashion or portrait photographers, who generally have the flash close to their subject, HSS is an excellent option. The ELB 500 TTL is a perfect mix of power and portability with HSS and TTL technologies built-in.
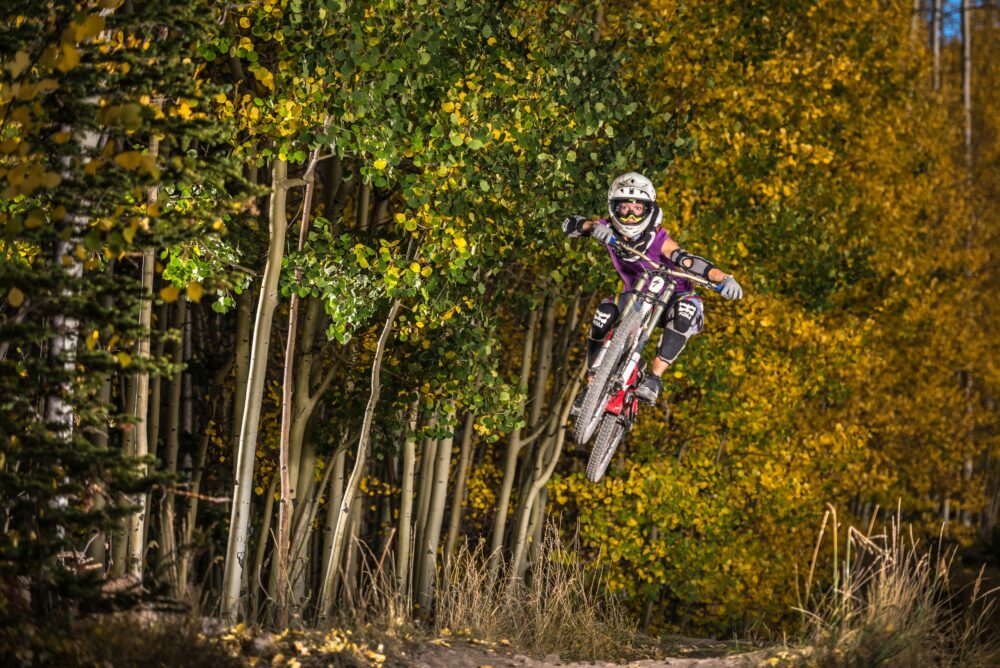
This portrait of a whitewater kayaker was created using one Elinchrom ELB 500 battery-powered unit in HSS mode with the TTL engaged.
The beauty of HSS
The beauty of HSS, and especially with TTL, is that you can quickly get an accurate exposure at any shutter speed and aperture setting and then move over to manual exposure flash mode and tweak the lighting as needed.
HSS automatically compensates if you change your shutter speed.
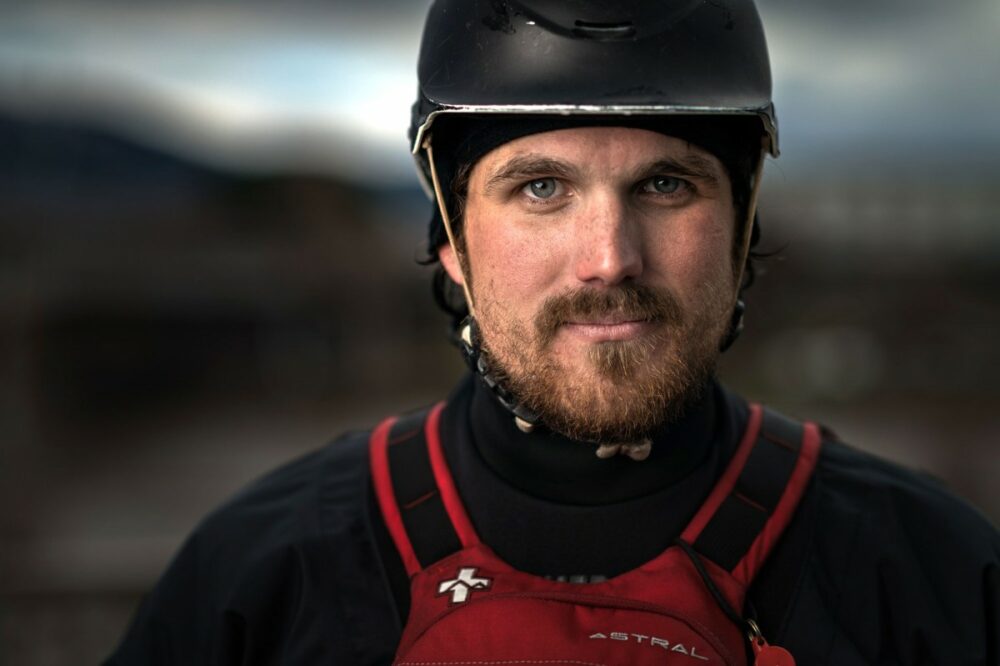

ELB 500 TTL - 1/4000th sec - f/2.2 - ISO 100
Hi-Sync (HS)
Hi-Sync is Elinchrom’s perfected version of HyperSync, which works in a completely different manner than HSS. To allow for the best results, the flash tube in the HS flash heads was optimized and dialed in the timing exactly for the Elinchrom flash units into the Transmitter Pro so that it works flawlessly.
In short, Hi-Sync (HS) has been perfected on a level that solves many issues of other technologies. Because of this, the HS works at any and all power settings on the ELB 400 and the ELB 1200 when using the respective HS flash heads.
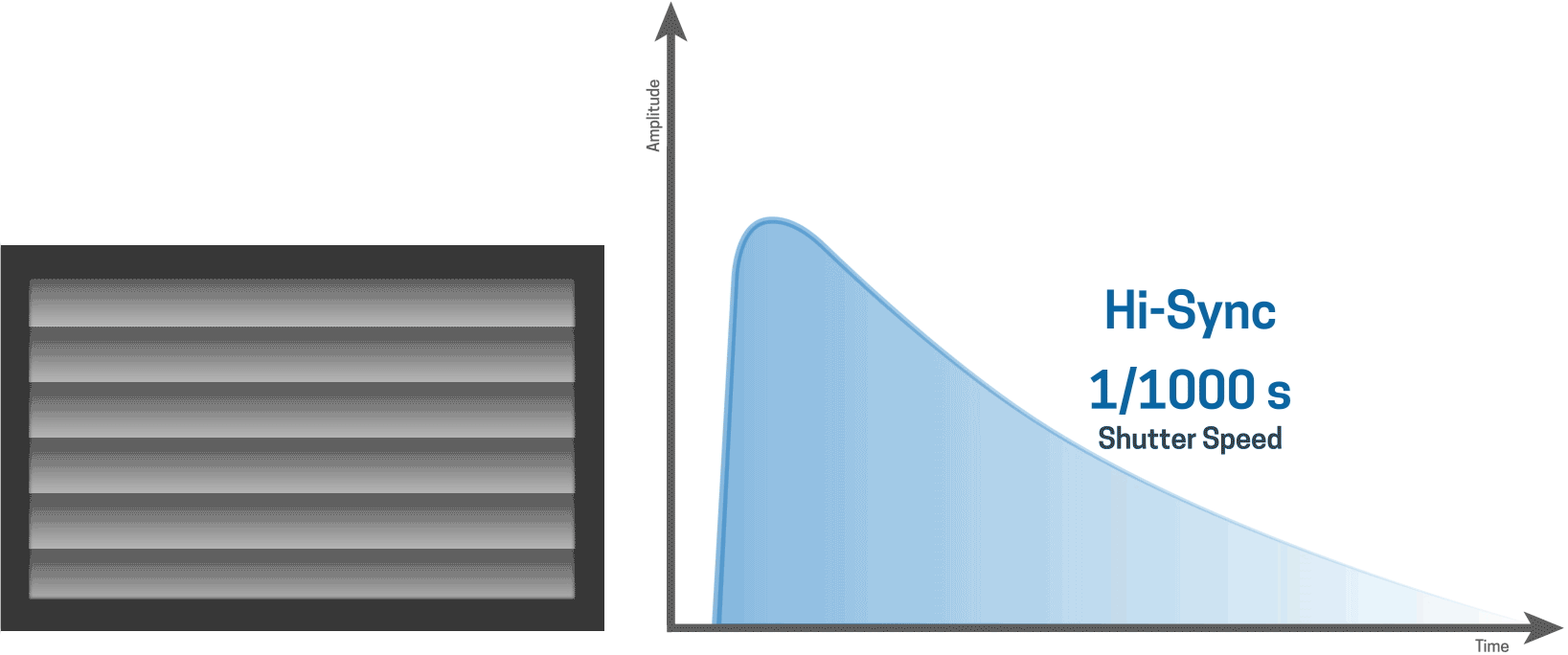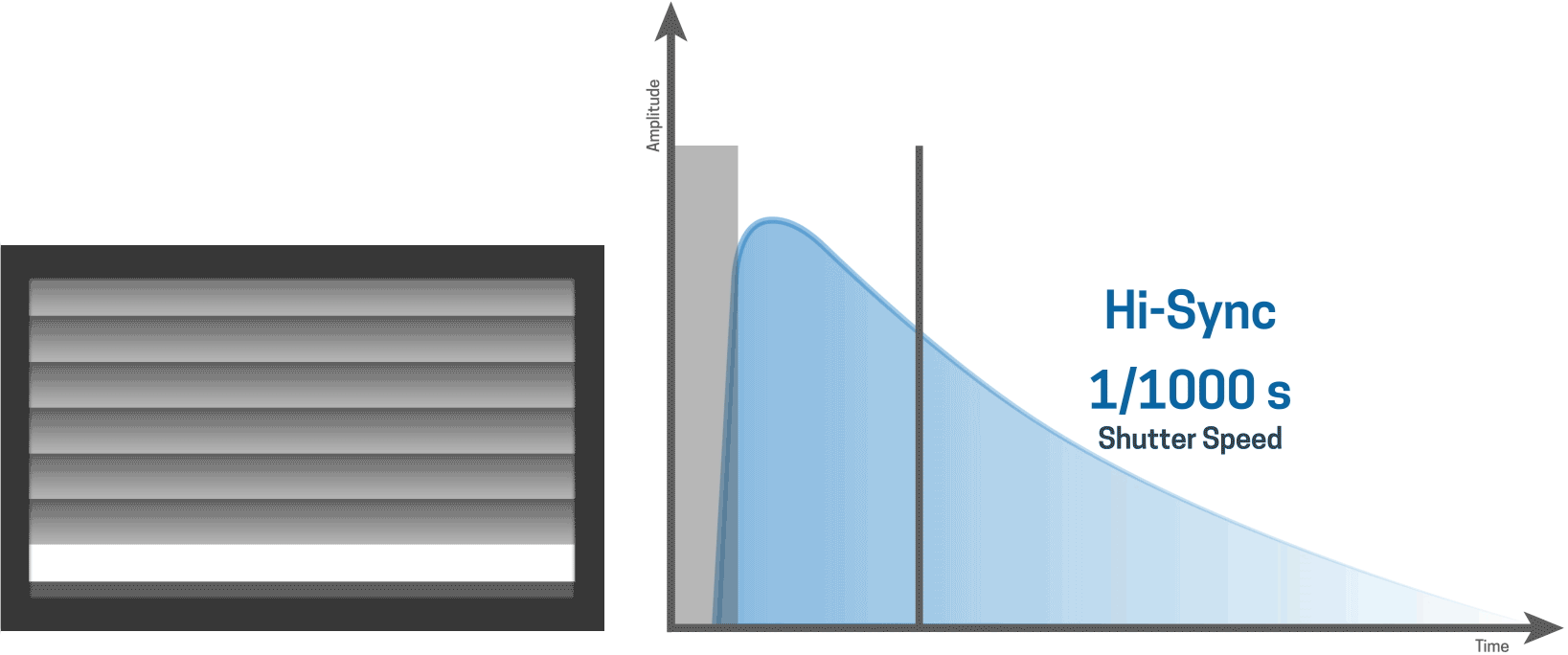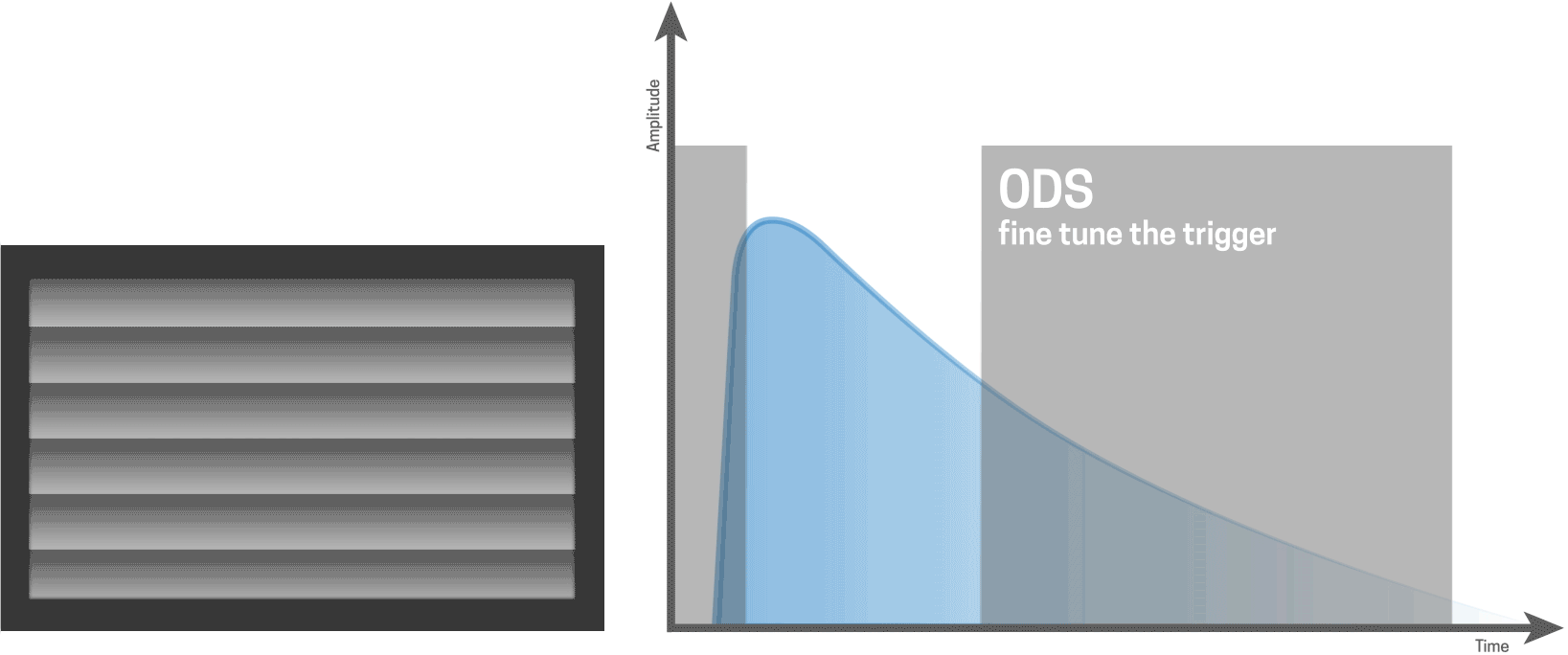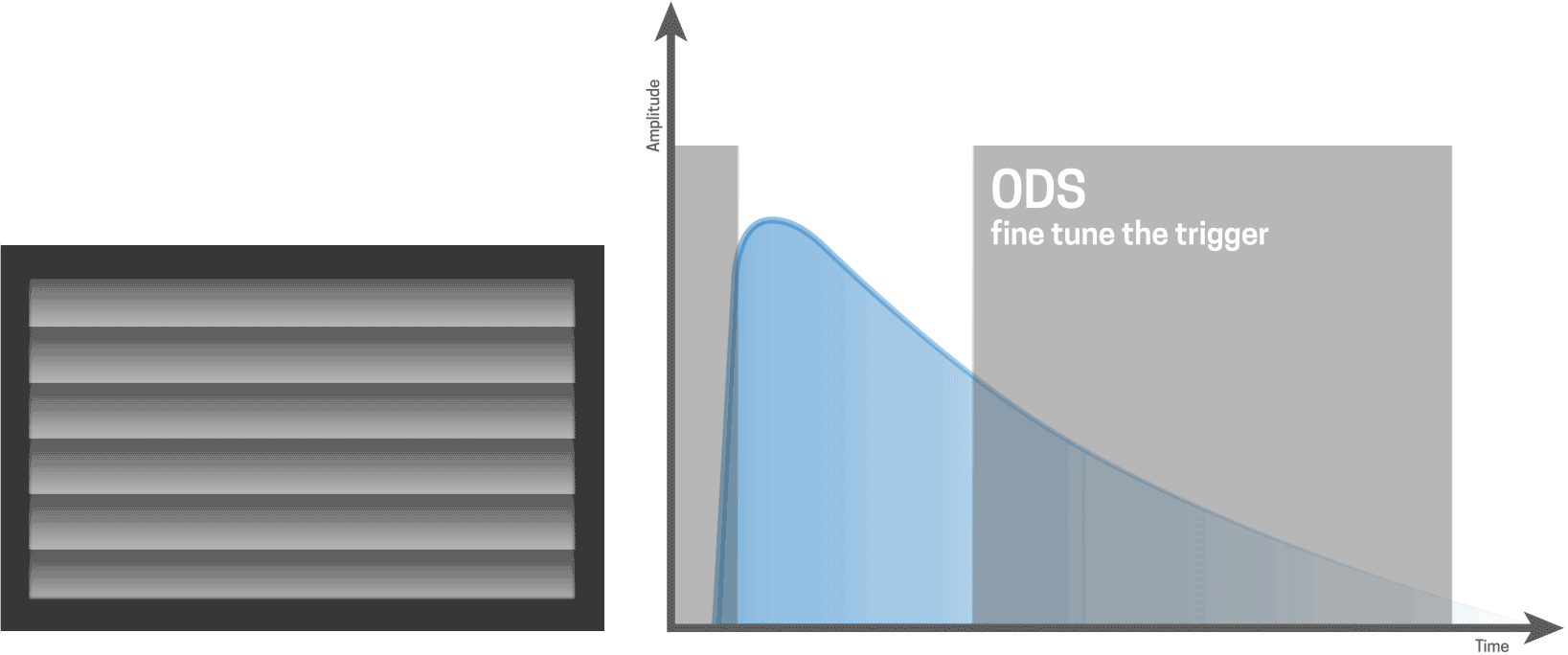
With Hi-Sync, it is very easy to take the best slice of the light out of the flash curve. The ODS feature helps you to fine tune and select the precise moment of your trigger.
Hi-Sync technically triggers the flash before the camera shutter fires and uses a normal flash mode. HS works best with slower flash durations so that the transmitter can sync up the timing.
When used with flash units that have a faster flash duration it is much more difficult, if not impossible, to time where and how the slice of light is taken out of the flash curve. Hence for the best results with HS, using the HS flash head for your ELB unit is highly recommended.
When using HS, a gradation is common.
With the Transmitter Pro and the ELB 400 HS flash heads, which have a flash duration of 1/550th second at full power, there is a very little gradation that can be seen in the images all the way up to 1/8,000th second.
When using the ELB 1200, the gradation is more apparent. Regardless, this gradation is incredibly easy to correct in post-processing.

A gradiation when using HS
The benefits of Hi-Sync
The benefits of Hi-Sync include the ability to sync at shutter speeds above your normal sync speed, freeze motion, and the ability to overpower the sun from phenomenal distances. Hi-Sync can also be used to create a narrow depth of field using large apertures. Hi-Sync is fairly easy to use once you have it dialed in for your camera, though it is not as easy to use as HSS with TTL.
Hi-Sync is by far the best option for those who need the highest light output from their flash when shooting at shutter speeds above their flash sync speed. Hi-Sync also offers more options than any other flash technology because you have more light output at your disposal.
Because the ELB 400 and the ELB 1200 have multiple flash heads to choose from, and because the ELB 1200 has a Dock that turns it into a studio strobe, these two units are incredibly versatile.
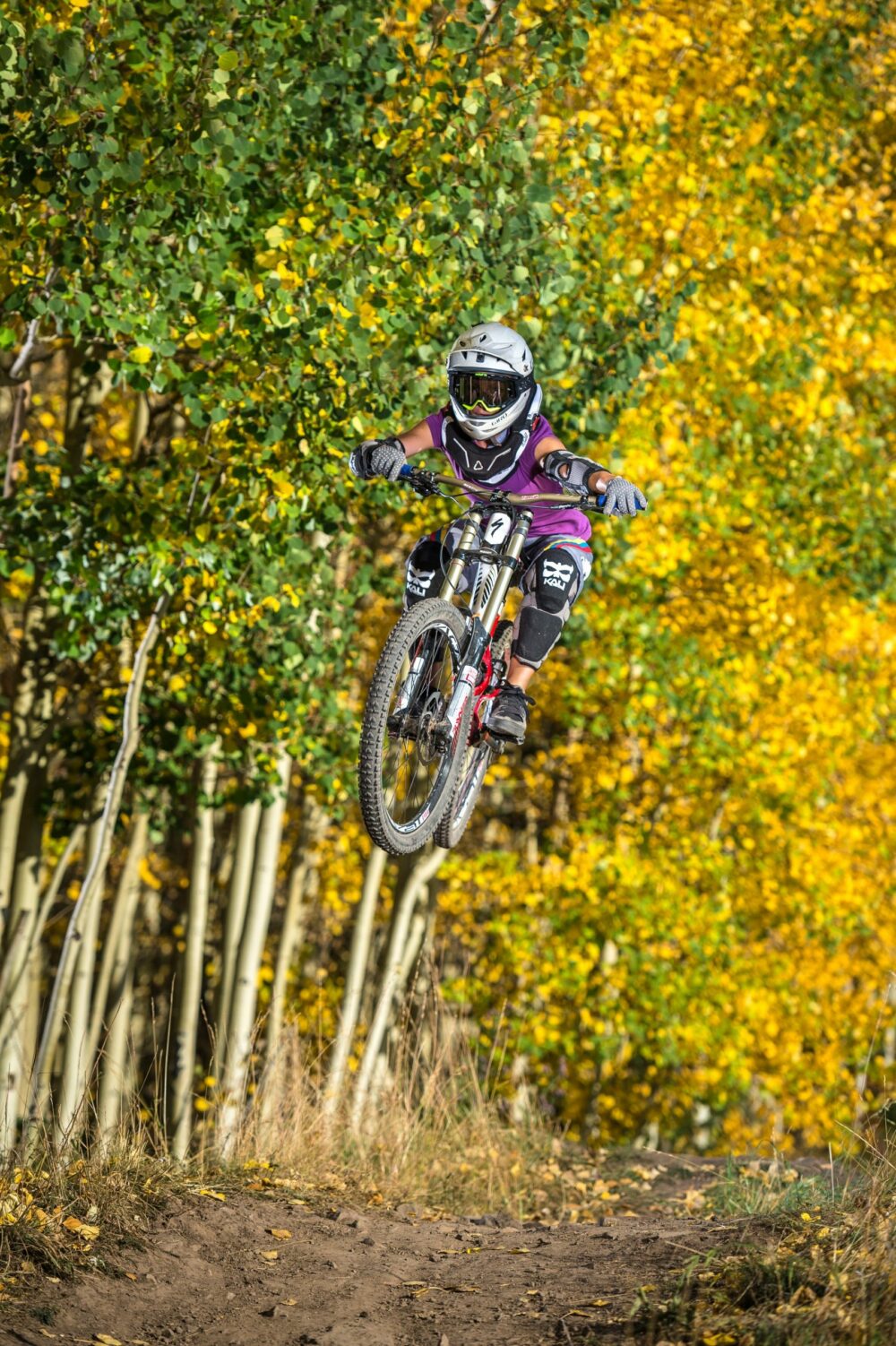

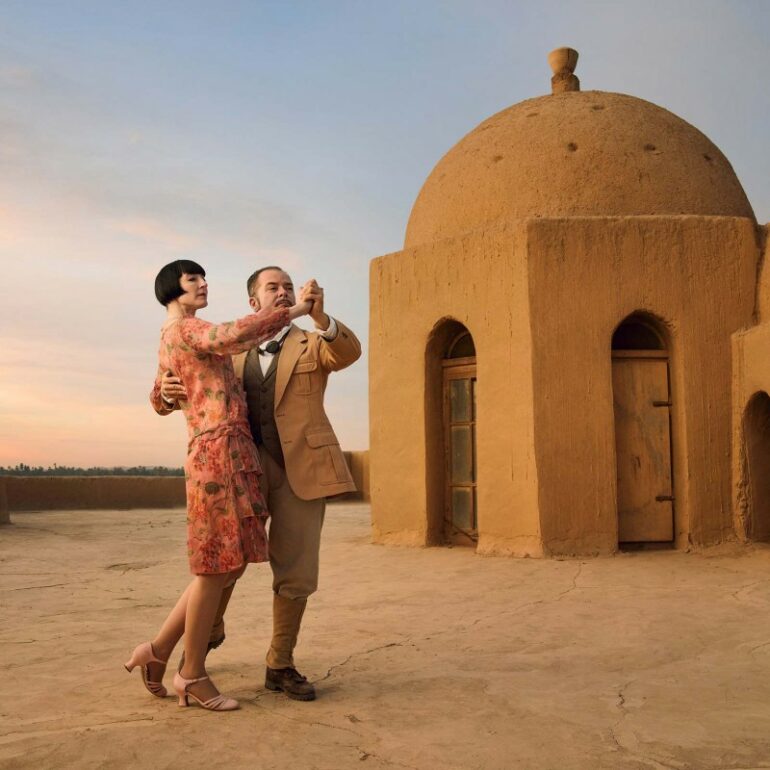
The sun was overpowered in the middle of the day from over 20-feet away to make the biker pop out of the image. 2x ELB 400 + Pro Head - 1/4000th sec - f/4 - ISO 200
Choose the right head
For those jumping into HS with either of these kits, I recommend the HS and Action flash heads to have the ultimate versatility.
When using higher shutter speeds, like those above your normal flash sync—i.e. 1/400th second up to 1/8000th second, the HS flash head is the one to work with. When using shutter speeds at or below your normal flash sync shutter settings—i.e. 1/250th second down to 30 seconds, the Action head is then the preferred option because it has a very fast flash duration.
In the former case, the shutter speed will stop any motion and in the latter case, the fast flash duration will freeze the motion of the subject.
Hi-Sync uses much less power than HSS because the flash head is firing normally. With Hi-Sync it is also possible to turn the power down and continue to use a fast shutter speed. Hi-Sync offers more versatility than any other flash option on the market.
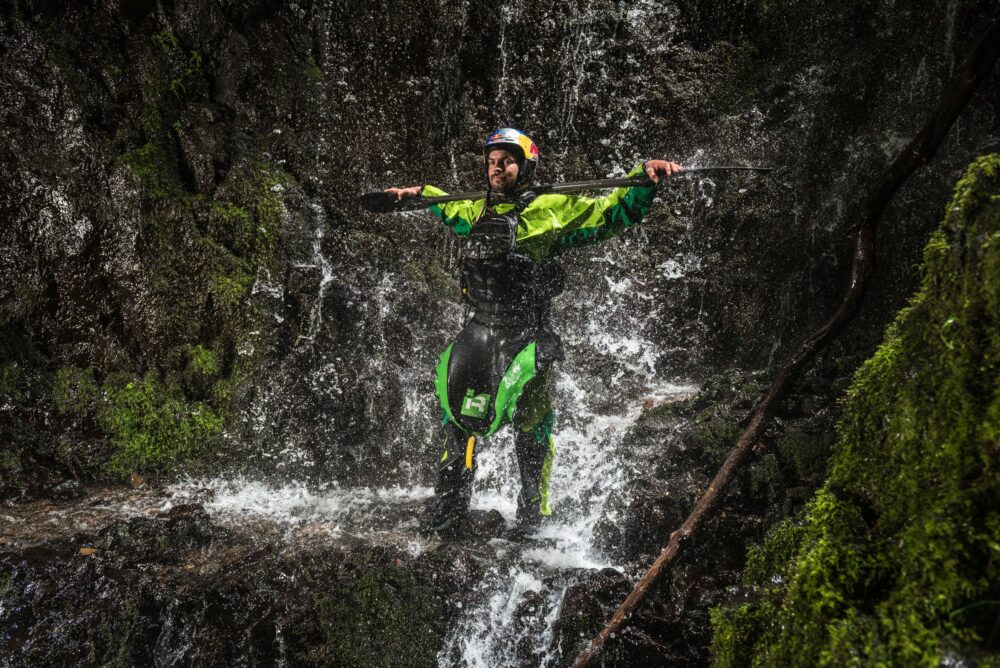

ELB 1200 + HS flash head - 1/2500th sec - f/5.6 - ISO 400






